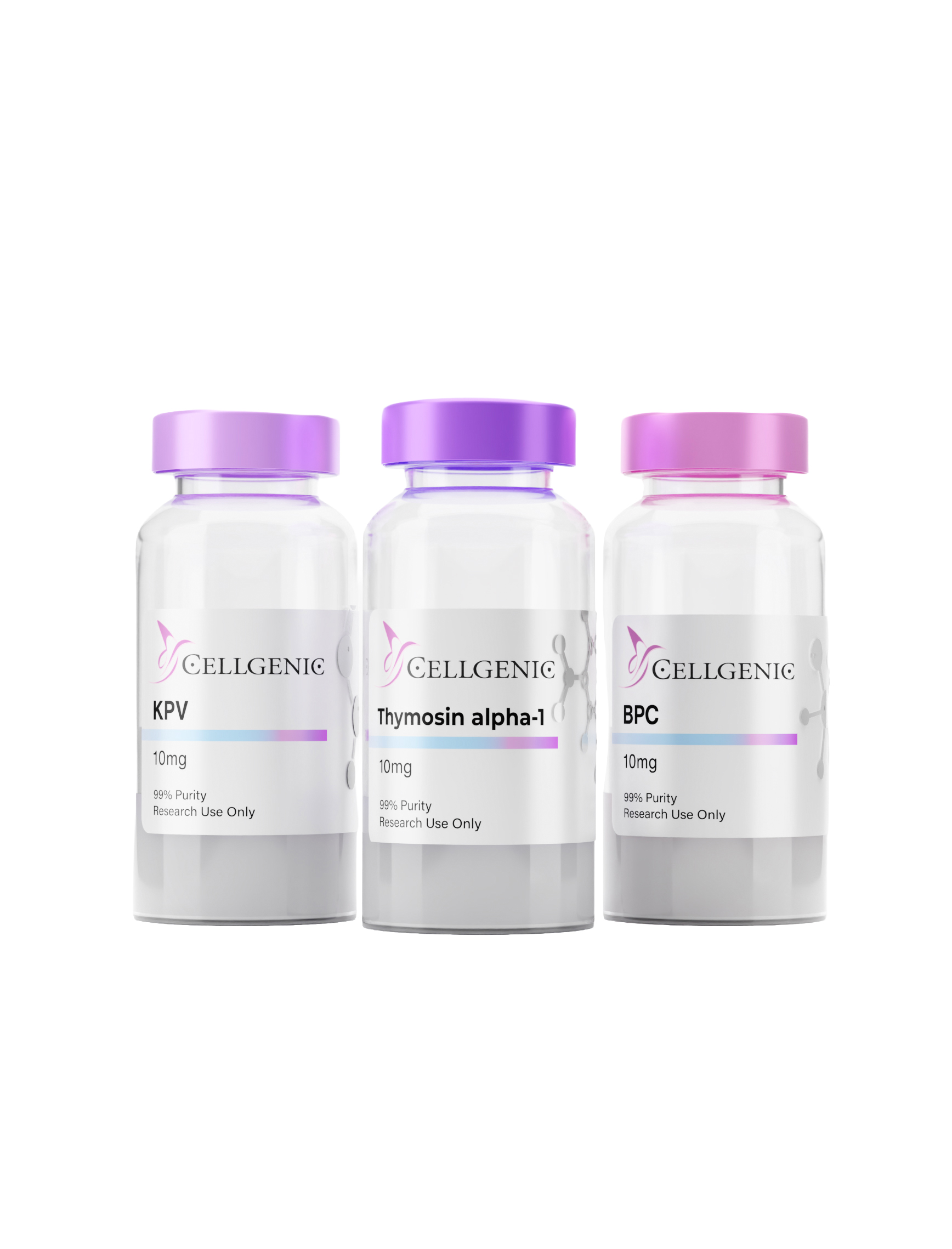
Thymosin Alpha-1 (TA1)
Mechanism: A naturally occurring thymic peptide that functions as a Toll-Like Receptor 9 (TLR9) agonist. It is critical for the maturation of T-cells (thymopoiesis) and the upregulation of MHC Class I molecules. Clinically, it restores the Th1/Th2 balance, shifting the immune system away from allergic/autoimmune reactivity (Th2) and toward effective antiviral and anti-tumor defense (Th1). It is the gold standard for treating “immune exhaustion.”
KPV (Lysine-Proline-Valine)
Mechanism: A potent anti-inflammatory fragment of $\alpha$-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone ($\alpha$-MSH). KPV works by inhibiting the NF-$\kappa$B pathway (the master switch for inflammation) within immune cells. It is particularly effective for patients with Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (CIRS) or mold toxicity, as it stabilizes mast cells and reduces the systemic hypersensitivity often seen in these conditions.
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound)
Mechanism: While known for tissue repair, BPC-157’s primary role here is cytoprotection of the gastrointestinal mucosa. By repairing “tight junctions” in the intestinal lining (treating “Leaky Gut”), it prevents the translocation of bacteria and lipopolysaccharides (LPS) into the bloodstream. This reduces the chronic background inflammation that distracts the immune system, allowing TA1 to function more effectively.